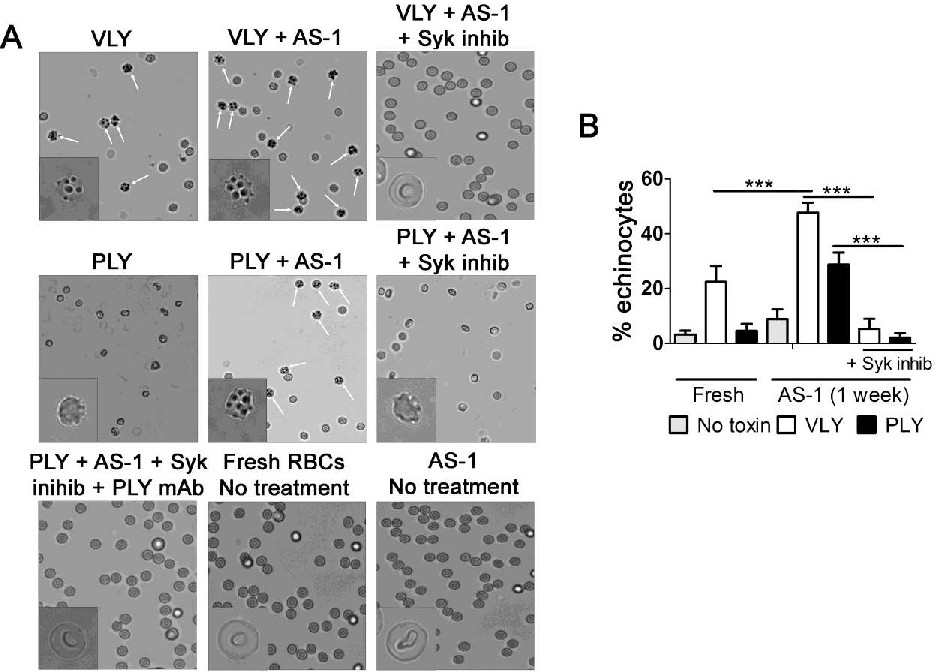
Fig. 7. RBC storage leads to Syk-dependent echinocyte formation. A.) Fresh human RBCs or those stored for 1 week in AS-1 were treated with the necroptosis-inducing toxin, VLY, or the non-necroptotic PLY. VLY induces echinocyte formation in fresh RBCs (arrows) while PLY does not. Echinocytes increase following 1 week of storage in response to either toxin. This increased echinocyte formation following storage was prevented by inhibition of Syk kinase (Syk inhib). RBCs were still affected by PLY following Syk inhibition but no echinocytes were observed. Treatment of these cells with a neutralizing mAb against PLY returned RBC morphology to normal. Representative images from 3 independent experiments are shown. B.) Quantification of echinocyte formation. Results shown are from 3 independent experiments. 10 fields were counted in each experiment. Two-way ANOVA, ***p<0.001.